Balanced GPU Solution in Composability and Performance
AI productivity and GPU utilization rate are crucial
Even for enterprises, high-performance GPUs and AI experts are considered very expensive resources. Take Amazon as an example, one single unit of nVidia V100S costs the company $7,999 and the annual salary of an AI expert is $120K on average. Obviously, any AI or HPC company does not hire only one AI expert or use a single GPU to accelerate their computing process, thus how to optimize the use of these pricy GPUs to further increase the AI experts' productivity is an inevitable challenge for many enterprises.
HW composable capability to provide the required GPU on demand
There are two approaches to enhance the GPU utilization. It can be done either with software (SW) solutions such as GPU virtualization, or hardware (HW) solutions, which we are going to explore in this blog.
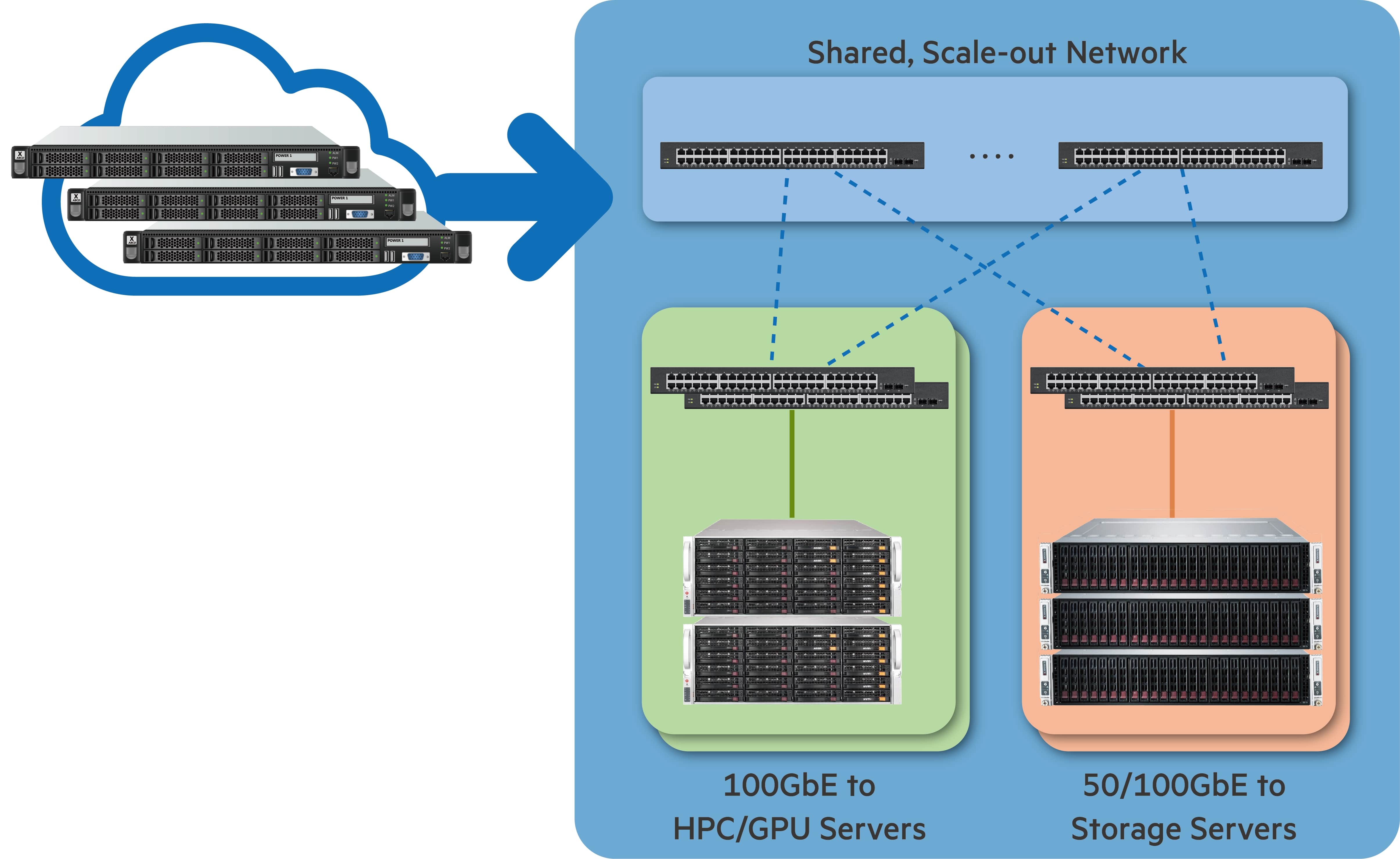
By HW approach, we mean composable GPU solutions, or so called "GPU pooling". GPU pooling is commonly achieved using InfiniBand or Ethernet, but Ethernet is not that ideal for scale-out and high-performance instances as the latency limits the GPU scale-out. On the other hand, the InfiniBand is widely used to achieve GPU pooling in cloud computing, where the GPUs can be accessed by the hosts with RDMA technology. The InfiniBand GPU pooling architecture appears to be more reliable, but also very expensive in equipment and operations.
a. Big-scale GPU deployment by using InfiniBand or Ethernet.
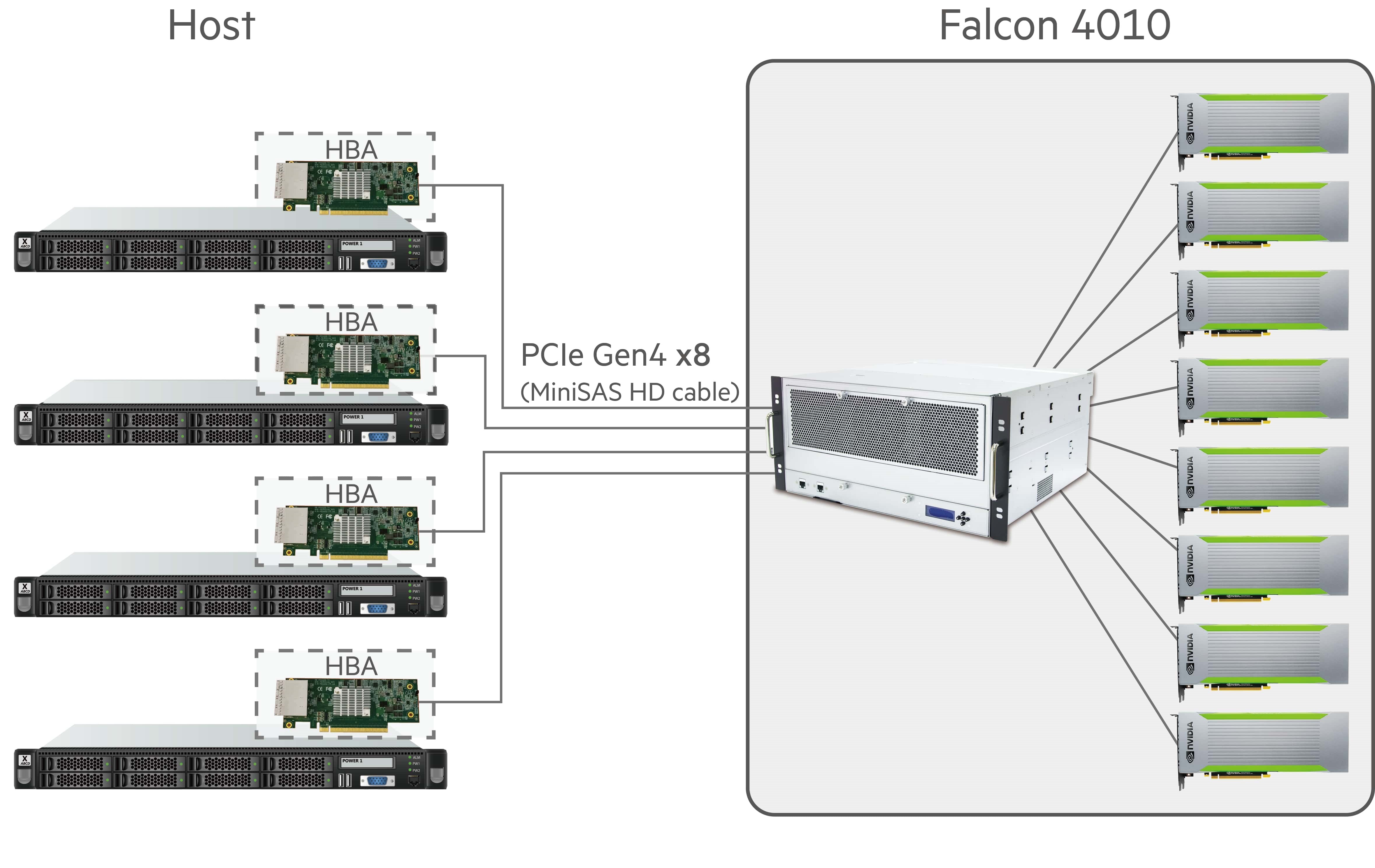
Aside from the Ethernet and InfiniBand, there is another cost-efficient way to achieve GPU pooling with PCIe fabrics. Every CPU and GPU have built-in PCIe fabrics, and the PCIe channel ensures lowest latency while keeping the cost of deployment low. But you might be curious about how exactly do we make composable GPU possible through PCIe fabrics? Let’s look at the diagram below.
b. 4-server deployment by using PCIe Gen 4 fabric.
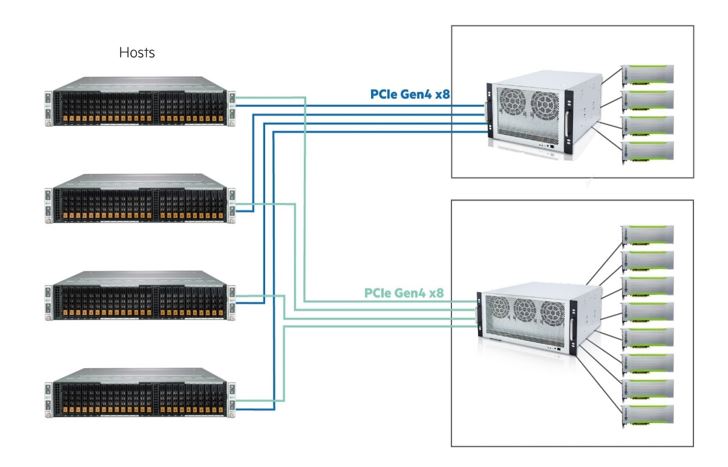
This diagram demonstrates how GPUs in the chassis can be dynamically provisioned to the connected hosts, one can easily assigne proper amount of GPU resources to meet the workload (e.g. AI training), and return them to the pool, making the resources available for new tasks upon work done. One thing to highlight here is that through PCIe protocol, the provisioned GPU units are treated as direct-attached devices to the host servers, therefore the interference in data transfer process due to channel is minimized.
An easy-to-use self-service tool is the key to composable GPU solutions
AI experts use GPUs for many different functions in different stages of developments, and the computing power, or the number of GPUs, required in different stages vary. For example, a single GPU may be enough in test-run while 4 or more GPUs are required in AI training, there are even stages, such as result investigation, where GPU is unnecessary. Due to these dynamic and complex GPU usage patterns, an easy-to-compose and self-service GPU pooling structure is a must for AI experts to efficiently utilize their limited GPU resources. Luckily, H3 Platform provides composable GPU chassis and PCIe device management UI integrated solutions for AI experts to overcome the difficulties in computing resource allocation.
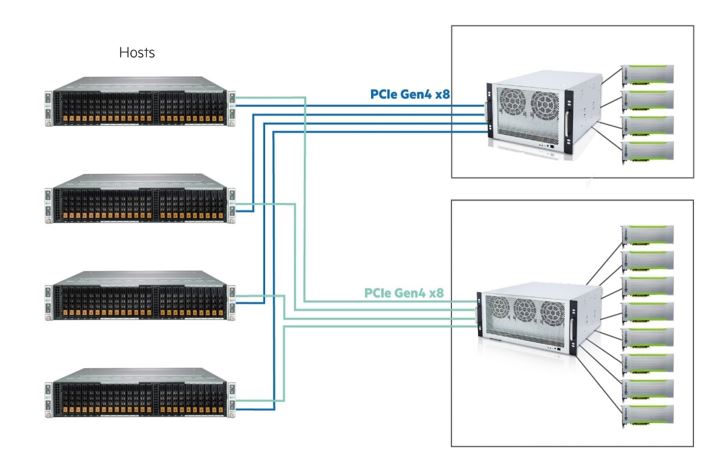
Cluster configuration of PCIe Gen4 GPU solution
This diagram demonstrates an average GPU configuration: the 4 hosts share 8 GPUs in the cluster. These GPUs can be provisioned to any connected host or returned to the GPU pool. At maximum, a host can get up to 8 GPUs when performing AI training.
Configuration:
- 4x host servers
- 2x GPU chassis and each chassis is with 4x GPUs
- Each GPU chassis provides 2 PCIe Gen4 x8 PCIe lanes.
In this example, PCIe Gen4 x8 is used to connect the hosts and GPU chassis by 2-meter MiniSAS cables
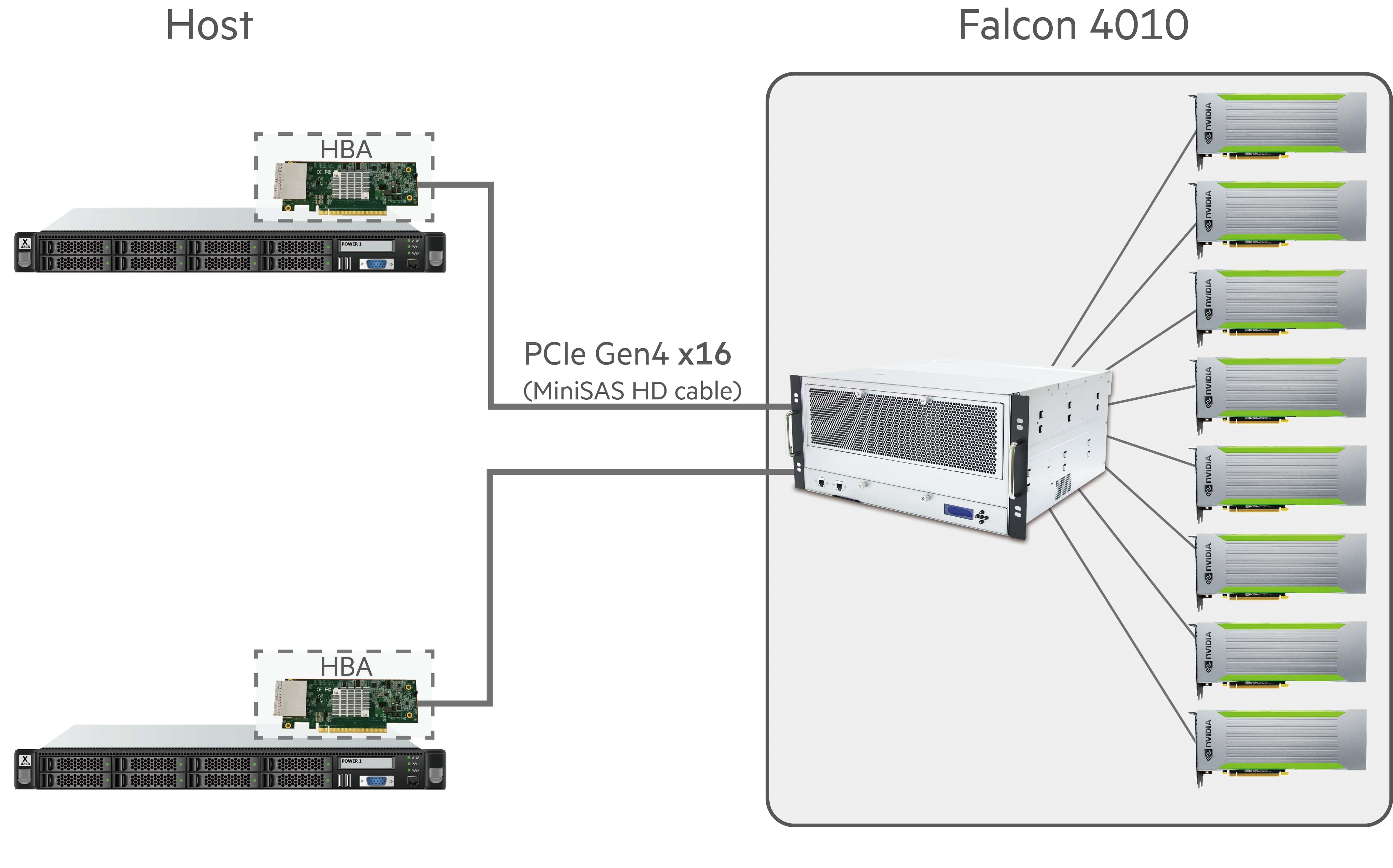
This diagram demonstrates a GPU configuration for higher performance: 2 hosts share 8x GPU in the cluster, PCIe Gen4 x16. 8 GPUs can be provisioned to any connected host or return to GPU pool. So, each host can get up to 8x GPUs when doing AI training.
Configuration:
- 2x host servers
- 2x GPU chassis and each chassis is with 4x GPUs
- Each GPU chassis provides 2x PCIe Gen4 x16 PCIe lanes.
In this example, PCIe Gen4 x16 is used to connect the hosts and GPU chassis by 2-meter MiniSAS cables
How to allocate GPUs to hosts and return them back to the GPU pool
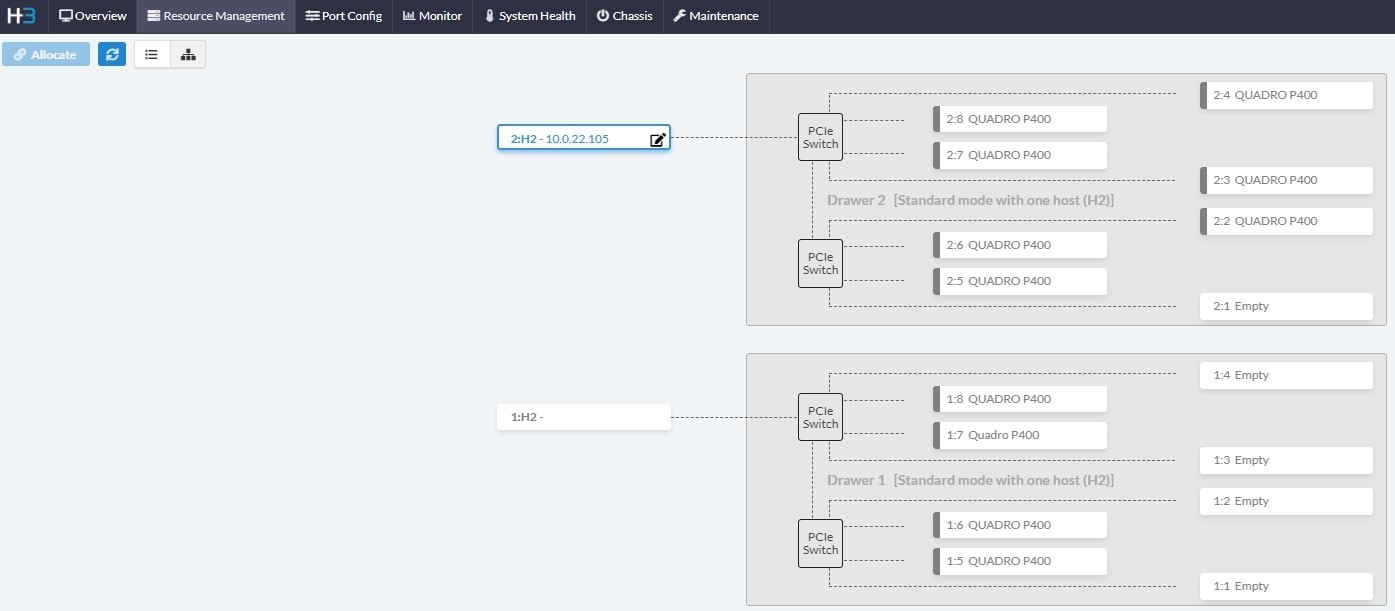
H3 Platform provides a user-friendly management UI to control all the GPU allocation activities. Users can easily configure and manage the GPU pool via a 1GbE management port.
a. H3 management center UI- GPU provision
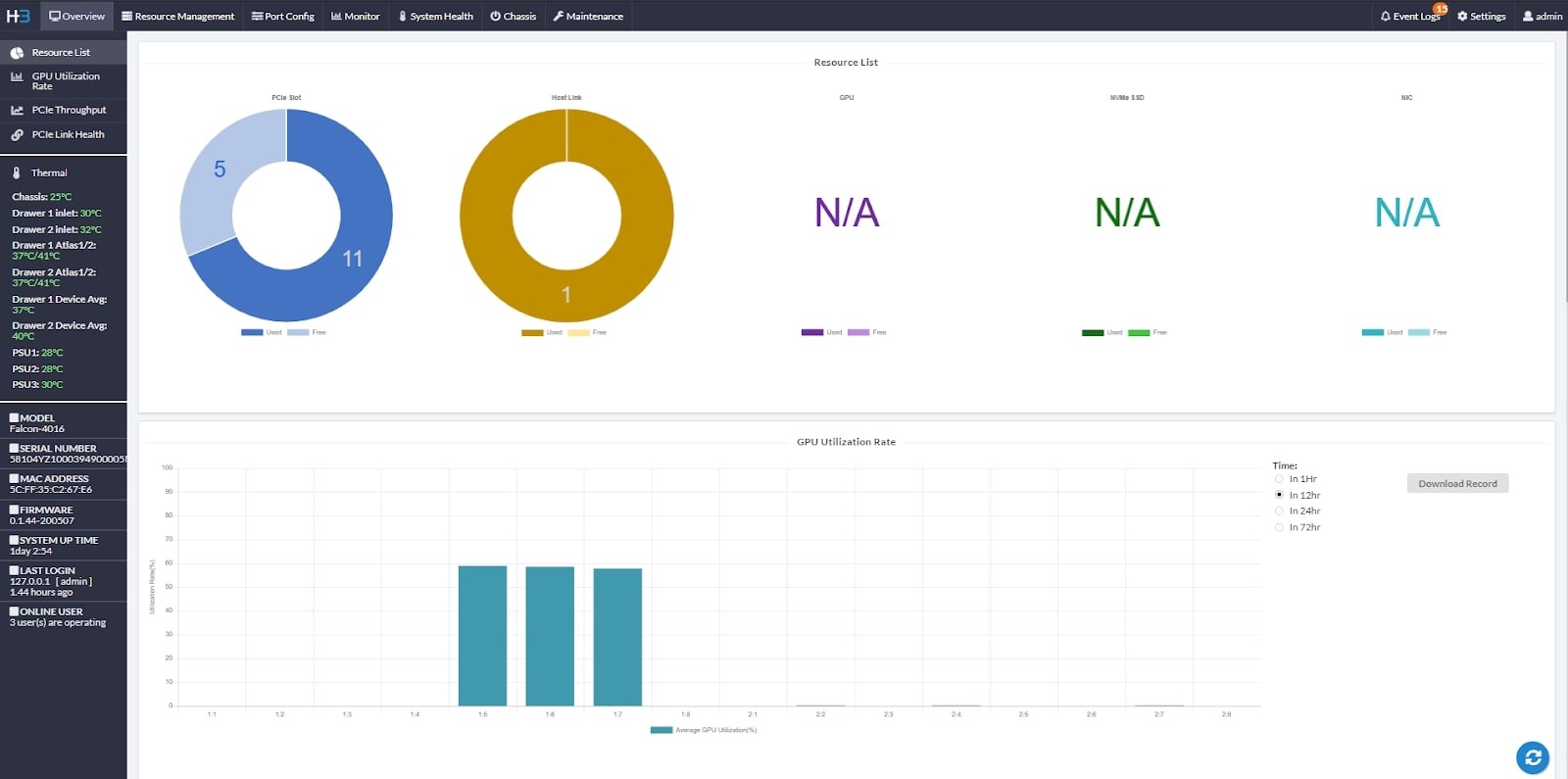
b. H3 management center UI- Resource performance
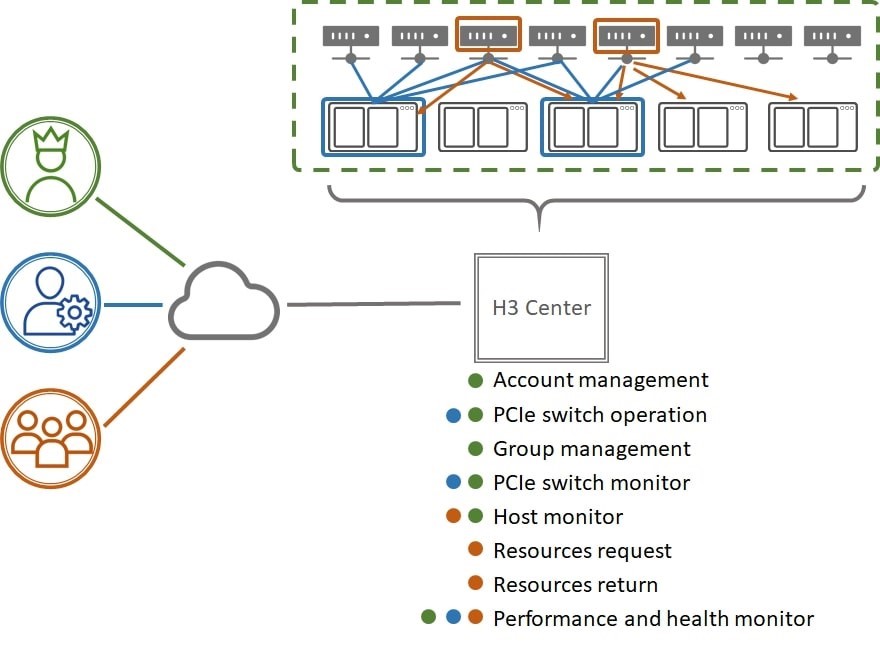
How to manage multi-GPU chassis in your network
Multiple GPU chassis may be needed for reasons such as more hosts are needed, more GPUs are needed, or special setups to meet requirements of a unique project. Fortunately, H3 managment center is capable of managing multi-units, supporting all the unique set-ups to meet the needs of different user groups.
Multi-chassis management on H3 management center
Building your own AI cloud by the newest PCIe Gen4 solution
Imagine a group of AI experts, looking to build their own AI environment with limited budgets on infrastructures. It would be impractical for them to purchase two separate high-performance servers where costs are high and GPU utilization cannot be optimized. On the other hand, the architecture of servers plus GPU pooling solution can significantly reduce the cost while increasing their productivity at the same time.