Cost-efficient Composable Infrastructure - Software, Physical, or Mixed Composable?

The hype of composable infrastructure has been all across IT industry in recent years, reason being that the datacenters have an urgent need of a solution that can accommodate the increasingly complex workflow, and you guess it, the whole idea of composable infrastructure works perfectly in the context.
What is Composable Infrastructure?
In our words, composable infrastructure means pooling and disaggregating IT resources from CPUs, connect them through some type of networking, and finally enable provisioning of these resources through software. With composable infrastructure, IT can deliver systems of desired performance to any workload, and the utilization of devices is significantly improved.
Evolution of Composable Infrastructure
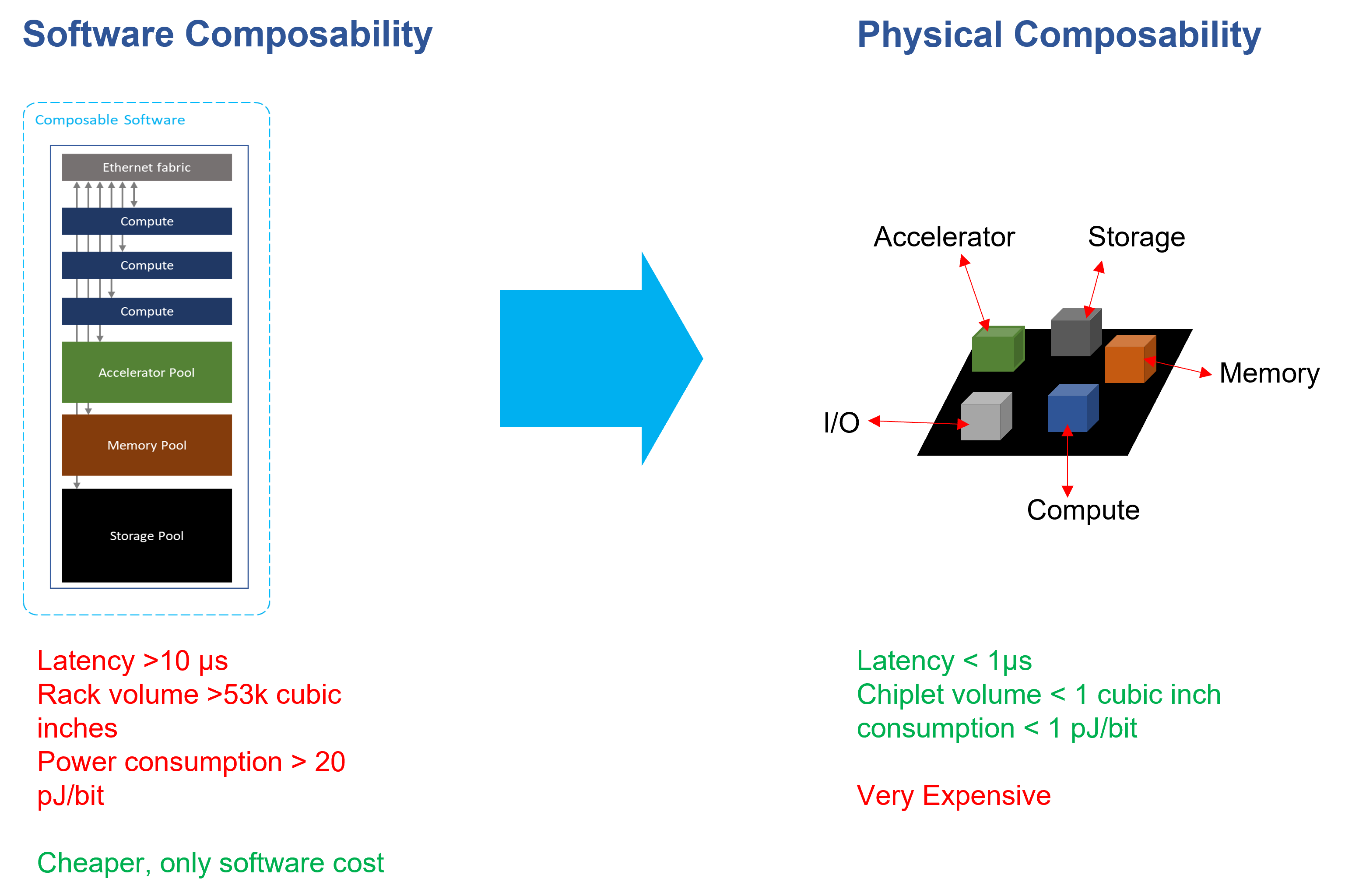
Reference: HPC-The Next Generation, by Allan Cantle.
The earliest composable infrastructures on the market focused heavily on software, virtualization, and was storage oriented. These first generation of composable infrastructure often uses ethernet fabrics as interconnect protocol, in order to keep up with computing performance, CPUs and accelerators were still coupled in a bare-metal server chassis, and that means only the storage was able to be provisioned, and the systems were delivered in virtual machines. Yes, the accelerator devices can also be decoupled and connected to hosts through ethernet network and being composed with software, but the performance drop due to network would be unacceptable to most users. Afterall, accelerators are much more expensive, and you wouldn’t want them to lose performance.
So, the shortcoming of pure software composable approach is quite obvious. Ethernet as interconnect adds much latency to data transfer and the software stacks creates much overhead. As a result, although the devices become much more flexible, the performance does not match that of a bare-metal server where the processors and storage are bind together.
Moreover, the pure software composable systems often lack focus on hardware designs. These systems usually come in a full rack, users are not able to scale these systems in fine grain, and the power consumption of such composable racks is nothing more efficient than the common computing systems.
In light of the performance issue, more and more companies are now developing solutions that enables composability by hardware, hyper-converged chiplets are made specifically to fulfill composable demands. There are several benefits with this physical composability approach, first being that the latency within the chip will be significantly lower than software composable systems where the data has to travel across racks. Next, the power consumption of chips will be significantly lower than that of a rack of hardware. Last but not least, by integrating composable necessities onto a single chip, the volume is significantly reduced, hardware that used to take several rack spaces now takes less than a cubic inch.
Physical composability seems fantastic, it seems to overcome all the issues that the software composability has. However, the biggest downside of physical composability is the cost. It isn’t easy develop a chip, not to say that it has to cover all aspect of composability. The R&D of these hyper-converged chiplet adopts the most advance technology and take much time and effort to complete. In addition, you might have to re-design the chip when the need changes even with only a little bit. As a result, the price of this kind of product would be very high. This physical composability approach primarily serves those large datacenters, medium and small organizations might not be able to afford this kind of technology at the moment.
Physical plus software composable
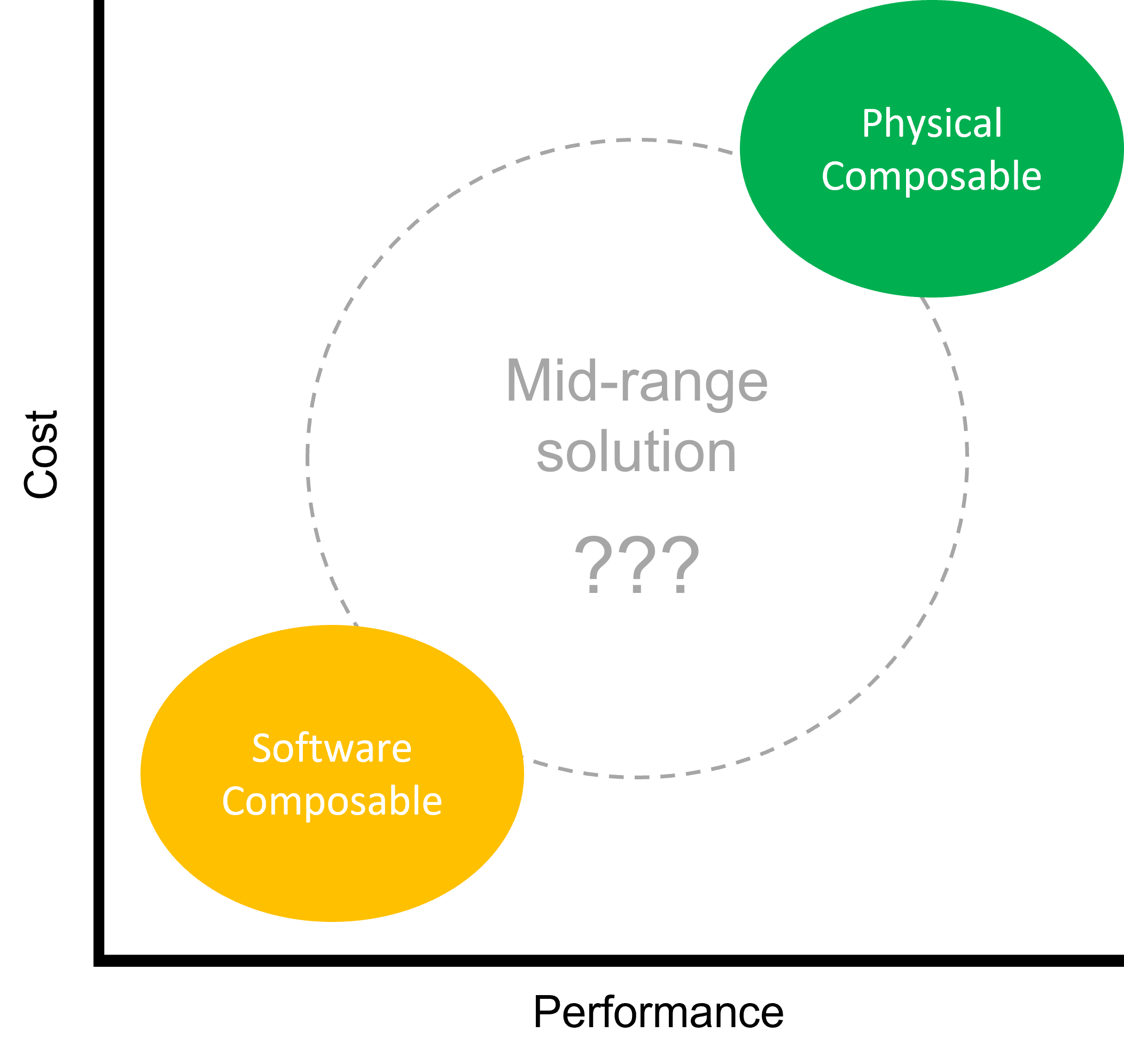
So, is there a solution that lands in between the two extreme methods to fulfill composability needs? If you have pay attention to Open Compute Project (OCP) you might have noticed a sub-project called Open Accelerator Infrastructure (OAI) and the Open Accelerator Module (OAM). You could visit here to check out more details on it. In short, the OAI introduces the OAM specification which modularize computing devices and adopts PCIe as unified interconnect to increase device pooling and power consumption efficiencies. Several OAMs are fit into a single chassis and linked by PCIe switches. That is to say, as long as the device is designed in OAM spec., whether it’s an accelerator, storage devices, or even the CXL memory expansion module (mind that CXL leverages PCIe buses), it can be physically mixed and match in the chassis according to user requirements.
Here is an example of node design with OAI chassis.
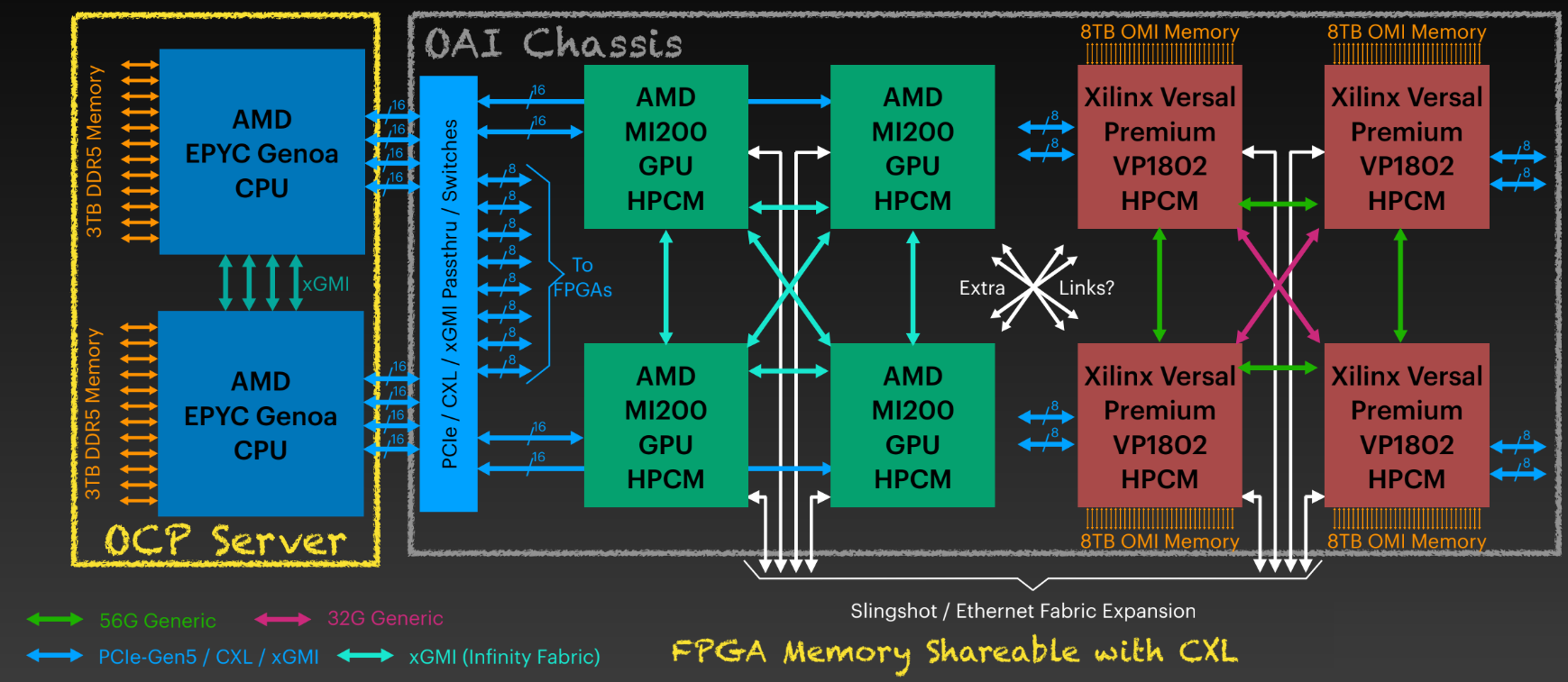
Image from: HPC-The Next Generation, Allan Cantle.
If you pay attention to the OAI chassis architecture showed in the above image and you will realize that it is quite similar to our Falcon Composable Solution.
- The device chassis is disaggregated from the CPU server.
- The PCIe switch/fabric is integrated to the device chassis.
- Unified connectors and communication protocol for devices.
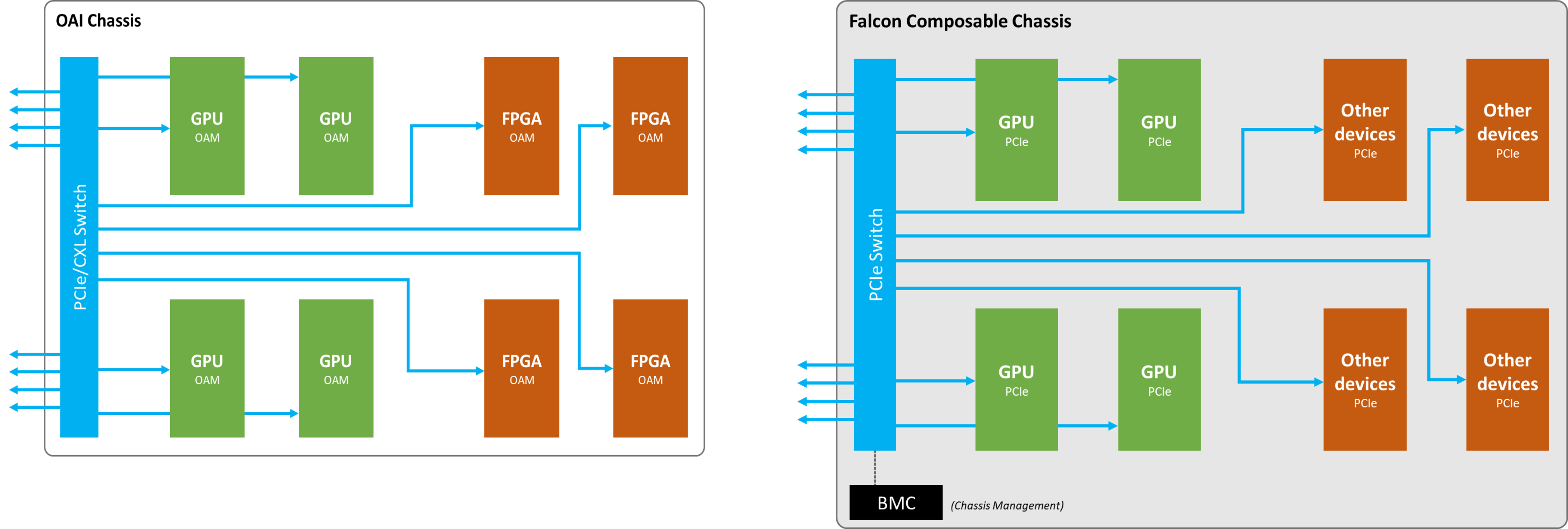
The idea is fundamentally the same and both adopts PCIe as the universal interconnect protocol. The only difference, really, is that the device from factor changed from PCIe slots (in Falcon composable chassis) to Mezzanine form factor in OAI chassis.
With H3 Platform’s experience in PCIe switch, it is totally possible to integrate a set of composable API to the PCIe switches in the OAI chassis to enable hardware composability of the OAM accelerators. By hardware composability, it means that there would not be extra software stacks that creates much overhead between the CPU and the devices, keeping the performance of disaggregated devices as if they were directly attached.
This hardware plus software composable approach fills the grey area between software and physical composability. It solves the performance and hardware volume issues that the pure software composable has with PCIe networking. In the meantime, since the hardware leverages existing technology, the cost to re-invent devices with standardized specification (be it PCIe cards or OAM) would be much cheaper than developing a brand new composable chiplet.
Yes, this physical plus software composable idea might not be as good as physical composable in terms of performance or it might not be as cheap as pure software composable, but it achieves good performance at more affordable costs. Most importantly, as we mentioned that this approach leverages all the existing technologies, not only that the solution can be developed in shorter time, but also it can be easily adopted by organization in any size.
Reference: HPC-The Next Generation, Allan Cantle, NALLASWAY Inc. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1oPcvd6AF95EmtbuFPRmURu5NW07ZlQQ7/view