Along with technological cloudification and the AI computing explosion, diverse demands such as large-scale data processing, real-time requirements, and heterogeneous hardware integration pose significant challenges. Particularly, avoiding performance degradation while processing massive datasets has become a crucial concern. Effectively managing memory resources has emerged as a pivotal solution, with H3's memory pooling solution playing a key role in addressing these challenges.
We will delve into a
comparative analysis of DDR5 SDRAM(Double-data Rate Fifth-generation
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) and DDR4, exploring how to integrate
these advanced technologies into our memory pooling solution. This endeavor
aims to enhance data processing efficiency with a flexible solution to navigate
challenges in this field.
Overview of Memory
Pooling Solution
H3's Memory Pooling
Solution is a memory expansion solution based on the resource composability
concept and aligned with the trend of Compute Express Link (CXL) protocol. It
leverages a resource management system to pool, dynamically allocate, and
flexibly partition memory based on application needs. After usage, the memory
resource returns to the pool for another reassignment. The free resource flow
breaks space limitations with heightened efficiency to reduce the overall TCO
(Total Cost of Ownership).
H3 Memory Pooling
Solution also incorporates the latest DDR5 technology with outstanding
transmission speeds of 7200 Mbps/s, significantly boosting bandwidth and
reducing power consumption. DDR5 can aptly address the growing requirements of
larger and more intricate data workloads. It delivers a performance boost of
more than twice that of DDR4, featuring a burst length increase from 8 to 16
and a doubling of banks from 16 to 32. This exceptional performance improves
the capabilities for processing extensive data and effortlessly manages the
demands of handling 8K content.
Imagine that integrating
DDR5 memory technologies into the CXL Memory Pooling Solution can deliver even
more robust performance. The data center capacity expansion and computational
capabilities optimization can further strengthen the multitasking processes
among even larger demanding workloads and foster next-generation innovation.
Next, we will briefly compare DDR5 and DDR4 on technical specifications and
performances and discuss their implications for memory pooling.
Comparison of DDR5 and
DDR4
Compared to DDR4, DDR5
brings substantial advancements, with a 50% boost in bandwidth scalable up to
8.4 GT/s, to facilitate accelerated data transfer rates. Operating at a reduced
voltage of 1.1V makes DDR5 achieve energy savings and decrease heat generation,
compared to DDR4's 1.2V. Its support for higher-capacity DRAM also allows
individual modules up to 256GB for enhanced memory capabilities, exceeding
DDR4's maximum of 64GB. Furthermore, with improved data transfer rates ranging
from 4.8 GT/s to 8.4 GT/s, DDR5 ensures swifter memory access.
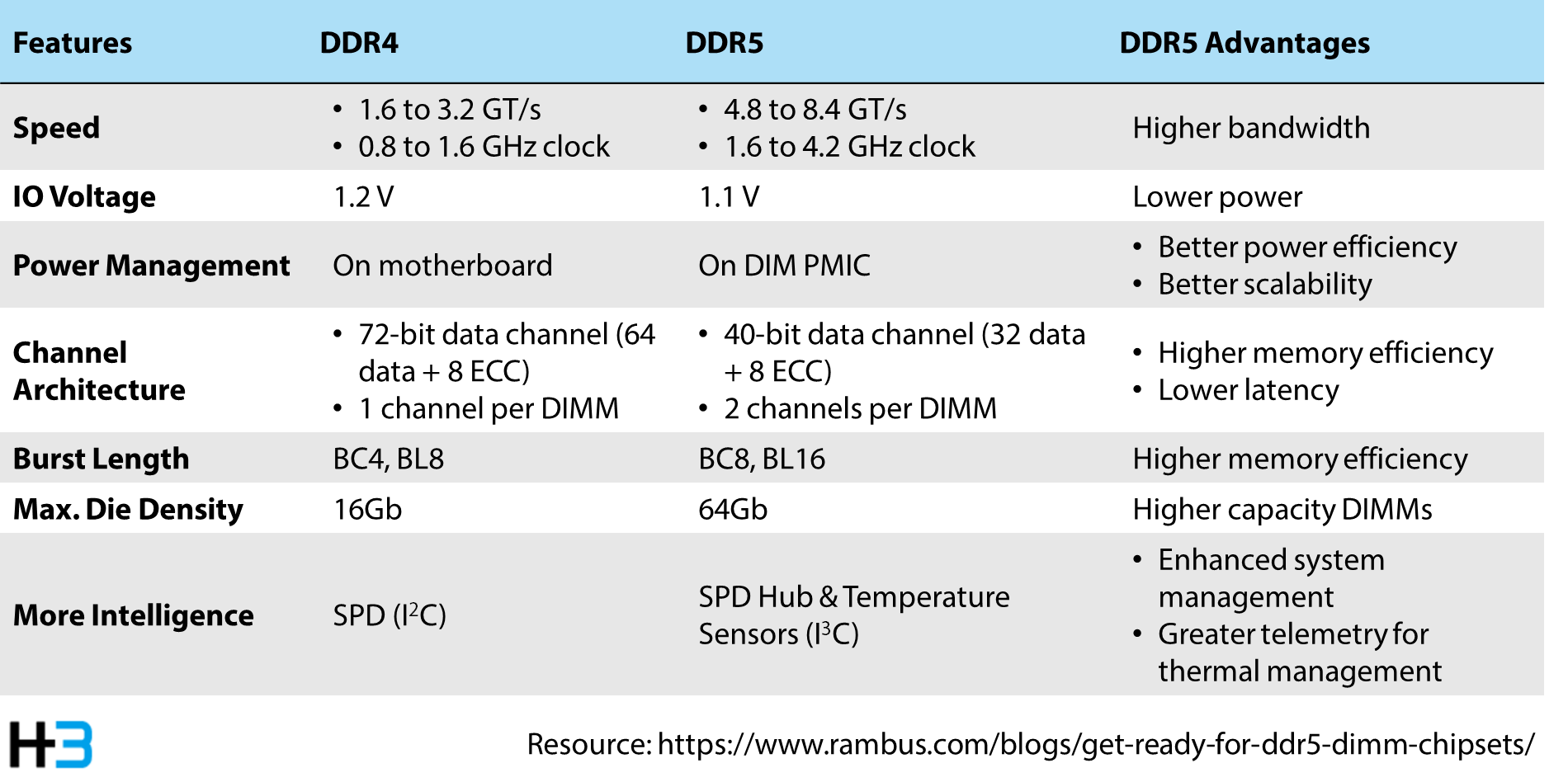
Although introducing a
new power management structure and DIMM channel overhaul in DDR5 improves
system power control and memory access efficiency, these advancements also pose
challenges to signal integrity. It requires users to consider power architecture
implementation.
In a word, DDR5 offers
superior performance and power efficiency, making it ideal for gigantic and
more intricate data processing workloads. Applications such as machine learning
and massive data analytics benefit from DDR5's increased bandwidth, expanded
capacity, and lower power consumption, collectively elevating system
performance to meet the escalating needs of data processing. Careful
consideration of application requirements is essential for optimal memory
standard selection.
Use Case of DDR 5:
Implications for Memory Pooling
In large-scale machine
learning training, the choice of memory in Memory Pooling solutions plays a
crucial role in system performance. For instance, when training extensive
neural network models, DDR5 technology offers tangible advantages over DDR4. As
mentioned, DDR5 provides higher bandwidth, accelerating the transfer of massive
datasets, especially when processing large weight matrices, thereby reducing
data transfer bottlenecks and improving model training speed. Additionally,
DDR5's operation at a lower voltage helps reduce the overall system power
consumption and heat generation, maintaining system stability, which becomes
particularly critical in scenarios involving prolonged and intense
computations. Therefore, for large-scale machine learning applications,
adopting DDR5 technology in a Memory Pooling Solution delivers faster data
access while effectively lowering system power consumption, resulting in higher
performance in real-world applications.
Therefore, the
advancements in DDR5, encompassing higher memory bandwidth, lower power
consumption, heat generation, and faster data transfer rates, hold significant
implications for Memory Pooling Solutions. It signifies the capability to
handle large and complex data processing workloads without increasing the
overall system's power burden. The higher data transfer rates of DDR5 in Memory
Pooling accelerate data sharing and transmission among memory, thereby
enhancing overall system efficiency. Moreover, modern memory technologies have
surpassed traditional architectures, providing larger memory capacities to the
disaggregated resource pool. A single DDR5 module supports up to 256GB of DRAM.
In the latest Memory Pooling design, the system can accommodate up to 8x DDR5
modules in a single Amber memory box, allowing for a maximum system capacity of
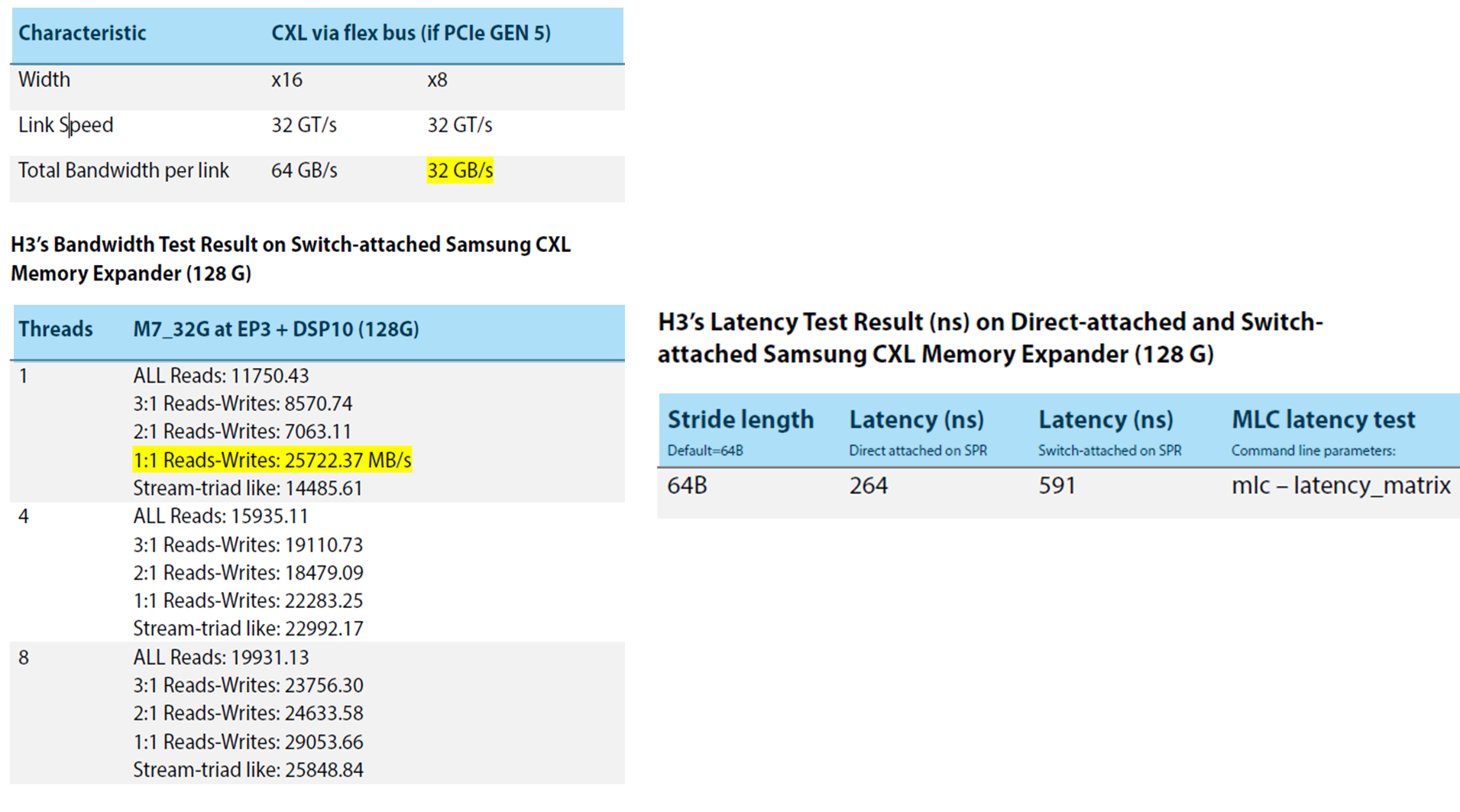
2TB. Our previous testing results reveal the bandwidth of switch-attached
memory is close to the ideal benchmark(26GB/s compared to 32GB/s), and the
latency test stands in the reasonable range (591 ns compared to the
direct-attached test result 264 ns). It implies that users can further expand
the overall capacity of the memory pooling, efficiently running large-scale
applications and realizing the advantages noted above.
Broadened Applications
through Integrating with FPGA, GPU, and More
H3 is expanding the CXL
Pooling Solution to incorporate FPGAs and GPAs, aligning with the current
integration of the CXL Composable solution. This extension harnesses the
technical advantages of high-performance parallel computing of accelerators
like FPGA and GPA, trying to boost high-performance computing capabilities,
system flexibility, and processing efficiency to meet evolving application
requirements.
Like earlier PCIe
Composable GPU solutions, the CXL Composable solution offers flexibility and
configurability for dynamic accelerator configuration. Its low-latency
communication enhances efficient communication among accelerators, improving
overall system responsiveness. The composable infrastructure allows multiple
applications to share and optimize hardware resources more effectively.
This integrated approach
facilitates the birth of a multifunctional hardware platform, expanding the
system's application scope. The flexibility to configure computational
resources based on specific needs enables a balanced optimization of
performance and power consumption. The adoption of a unified hardware
governance interface simplifies overall management and configuration.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving tech
landscape, H3's Memory Pooling Solution presents a strategic answer to
challenges in real-time data management and hardware integration. Anchored in
the composable solution concept and aligned with the CXL protocol trend, this solution
effectively manages memory resources.
Incorporated with DDR5
technology known for exceptional performance, data processing efficiency
significantly soars in the CXL memory pooling solution. DDR5's higher
bandwidth, reduced power consumption, and increased memory capacity make it
ideal for handling massive data workloads, especially in applications like
machine learning and analytics.
The implications of DDR5
on Memory Pooling Solutions reveal a capability to handle substantial workloads
without compromising power efficiency, accelerating data sharing within Memory
Pooling. Integrating FPGA and GPA into the CXL Pooling solution further
amplifies computing capabilities, ensuring flexibility and efficiency for
evolving applications.
In summary, H3's approach
addresses current challenges and lays the foundation for future advancements.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies propels Memory Pooling Solutions
into enhanced performance, expanded application scopes, and simplified management,
creating a comprehensive computing infrastructure ready for dynamic application
demands.